Securities provide a way to raise capital for businesses and for wealth creation for investors. Listing of these securities by an organization is important to achieve these goals as it brings liquidity, and transparency to the transactions. Generally, companies list their securities on the domestic exchange. However, over time companies have started to look beyond borders for raising capital. Apart from the businesses, even investors started looking for new investment opportunities and geographically diversified portfolios.
Considering this the government reformed the legislation and allowed the Indian companies to raise capital through ADR (American Depository Receipts) and GDR (Global Depository Receipts) (explained below). Read on to know how you can currently list on a foreign exchange and how an Indian company can be directly listed on a foreign exchange.
Initial steps taken by the government
As mentioned above, to offer companies the benefits of listing on the foreign exchange, ADR and GDR were introduced. Similarly, IDR (Indian Depository Receipts) were introduced for the companies outside India to give them access to the Indian capital market. Currently, Indian companies can list their equity share capital abroad only through ADR and GDR, while they can get their debt securities through the issue of Masala Bonds or Foreign Currency Convertible Bond (FCCB). Now you must be wondering what ADR and GDR are.
What is ADR?
ADR or American Depository Receipts is a means by which companies incorporated in India can raise capital from American investors. It allows non-American companies to trade in American exchanges. Here, each ADR can be of one share, multiple shares, or a fraction of shares as deemed fit by the depository bank. Generally, ADRs are of two types:
- Sponsored ADR - These are issued when the non-American company enters into an agreement with a US depository bank. The company issuing shares to the public, deposits its shares with the depository bank to sell them in the US market.
- Unsponsored ADR - These are issued when the shares of a non-American company are traded over-the-counter. In this case, the company doesn’t have a legal agreement with the depository bank.
What is GDR?
GDR or Global Depository Receipts are the negotiable certificates through which an Indian company can make its shares available to trade on different global exchanges. It is divided into two sub-categories:
- Rule 144A - These are the GDRs that allow trading of non-American companies in the American market via the rule 144A of the Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) of the US.
- Regulation S - Those GDRs which help non-American companies to raise capital and trade in the European market only are known as Regulation S GDRs.
However, many people started raising concerns about not allowing Indian companies to directly list in the foreign jurisdiction. Considering this along with other things such as the internationalization of the capital markets, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), the Indian market regulator, formed a committee to address this issue.
What is direct listing?
The direct listing is a process in which a domestic company can get its shares listed on a foreign exchange without an intermediary. In this process, a company incorporated in India can directly trade its shares on the stock exchange of other countries without having to give them to a foreign depository bank.
On June 12, 2018, SEBI constituted the ‘Expert Committee for listing of equity shares of companies incorporated in India on foreign stock exchanges and of companies incorporated outside India on Indian stock exchanges’. The core objective of this committee was to
- Make recommendations for a suitable framework to carry out the direct listing process
- Examine various legal, operational, and regulatory constraints that an Indian company may face while listing on a foreign exchange and vice-versa
After its thorough review, the committee submitted its recommendations and report in December 2018, where it supported direct listing in the overseas market. Click here to read the full report.
However, you must know that the Ministry of Corporate Affairs is still working on the direct listing and is accepted to be implemented in the near future.
Benefits of direct listing
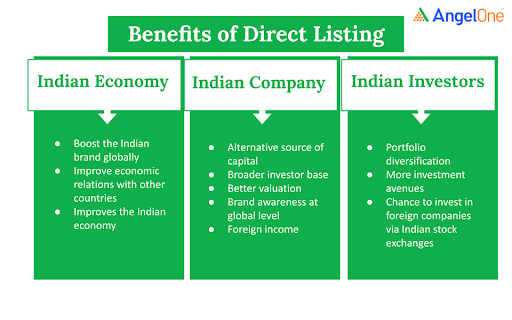
Issuing of securities in foreign jurisdictions has various benefits to investors, companies, and to the Indian economy.
Conclusion
As per current guidelines, Indian companies can list their shares on overseas exchanges through ADR and GDR which is helping them to raise capital through foreign markets. Once the direct listing is introduced in India, it will enable the companies to establish a better presence in the global market and give them an opportunity to trade at the international level. Other benefits that it offers to a company are - an alternative source of capital, a broader investor base, global brand recognition, better valuation, foreign income, and much more. Apart from these, it also helps Indian investors to diversify their portfolios while offering them an opportunity to invest in globally-recognised companies via Indian stock exchanges.
Learn Free Stock Market Course Online at Smart Money with Angel One.
Explore the Share Market Prices Today
| Tata Steel share price | Adani Power share price |
| PNB share price | Zomato share price |
| BEL share price | BHEL share price |
| Infosys share price | ITC share price |
| Jio Finance share price | LIC share price |
Disclaimer: This blog is exclusively for educational purposes only.

