You must have heard about the primary market and secondary market in the Indian stock market. But are you aware there are various types of issues allowed in the primary market? We will discuss these issuances in this article. Before we go any further, let’s first recall what is the primary market and what are its features.
What is Primary Market?
The primary market is a part of the capital market where the government, companies, and other institutions raise funds or capital by selling debt or other equity-related securities. The securities are sold for the very first time in this market because of which it is also known as the New Issue Market. Look at the below-mentioned features of the primary market:
- Shares, bonds, ETFs, or any other marketable securities are introduced for the first time in the primary market
- It doesn’t have physical existence as the secondary market has in the form of stock exchanges
- It precedes the secondary market as the securities float through this market before entering there
- It has various methods of raising funds
- It offers underwriting services and sells securities to investors
Types of issues in the primary market
Several types of marketable securities are issued under the primary market as represented below:
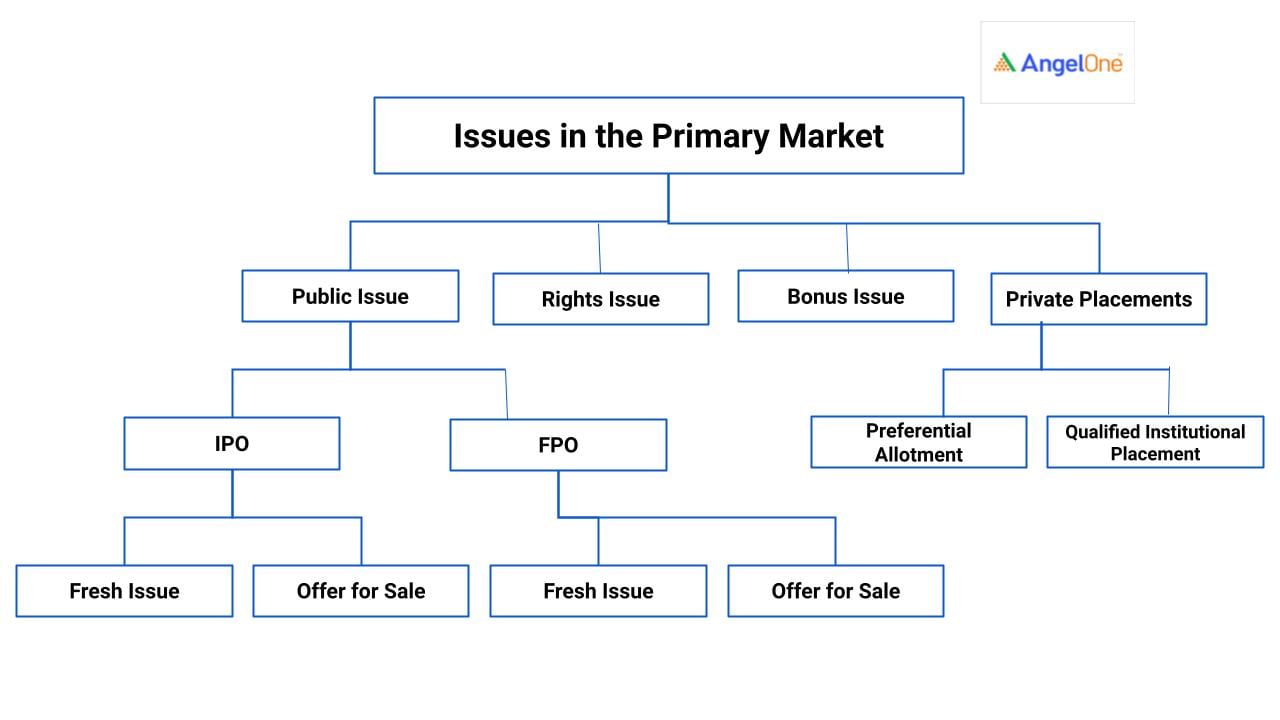
Now, let’s discuss each of the above-mentioned issuances in detail.
- Public Issue
One of the most common methods of issuing securities to the public at large is Public Issue. Generally, this process is undertaken by companies to raise funds from the capital market that can be used to expand their business, pay off debt, or any other reasons. You must note that these securities are further made available to trade on the stock exchanges.
A. Initial Public Offer (IPO)
IPO is the fresh issue of the equity shares or convertible securities by an unlisted company for the first time. A privately held company becomes a public company after it offers its shares via IPO. Once the process of listing is completed, the company’s shares are available to trade on the stock exchange.
B. Further Public Offer (FPO)
Also known as Follow on Offer, FPO refers to the process of issuing securities to the general public by the company which is already listed on the stock exchange. This is done with the aim to raise additional funds.
Both IPO and FPO can be undertaken by the company via 2 methods as mentioned below:
- Fresh Issue
It means the issuance of new securities in the company and selling of these new securities to the investors.
- Offer for Sale (OFS)
The selling of shares by promoters/investors of the company in order to reduce their stake is known as OFS.
- Rights Issue
The offer to the company's existing shareholders to buy new shares of the company at a discounted price is known as a Rights Issue. It invites its existing shareholders to avail fresh shares in the proportion of their holding in order to raise additional capital without going to the public at large.
- Bonus Issue
Bonus Issue is when a company issues fully paid additional shares to the existing shareholders in proportion to their existing holding for free. The issue is made by a company from its free reserves or securities premium.
- Private Placement
When a company sells its stocks or bonds directly to a group of people (private investors or institutions) instead of offering it to the general public is known as Private Placement. A company can raise funds quickly via this distribution strategy as compared to raising capital through fresh issues as the regulatory requirements are significantly less.
a. Preferential Allotment
The process in which the securities are allotted to a group of people/investors on a preferential basis at a specific price is known as a preferential allotment. Listed as well as unlisted companies can issue shares/convertible securities to a select group of investors via this strategy.
b. Qualified Institutional Placement (QIP)
A type of private placement in which a company issues shares of debentures (fully or partly convertible) or any other kind of marketable securities not including warrants (which are convertible) to Qualified Institutional Buyers (QIB) is known as Qualified Institutional Placement. Herein, QIBs are investors who have substantial financial knowledge and expertise to invest in the capital market. A few of the QIBs are mentioned below:
- Foreign Institutional Investors registered with SEBI
- Mutual Funds
- Public Financial Institutions
- Insurers
- Pension Funds
- Scheduled Commercial Banks, etc.
Issuing shares via QIP is simpler and quicker as compared to the preferential allotment as it doesn’t attract standard regulations like pre-issue fillings to SEBI.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, the primary market is a type of market where new securities are created and issued to the public by the company, government, and public sector institutions to raise funds. Being an investor or a prospective investor, you must have the necessary information about the primary market and types of issuances. The above-mentioned information will help you make a well-informed decision regarding investing in the market.
Explore the Share Market Prices Today
| IRFC share price | Suzlon share price |
| IREDA share price | Tata Motors share price |
| Yes Bank share price | HDFC Bank share price |
| NHPC share price | RVNL share price |
| SBI share price | Tata Power share price |
Disclaimer: This blog is exclusively for educational purposes and does not provide any advice/tips on Investment or recommend buying and selling any stock.

