If you’ve noticed once in a while you can see the news about companies going for mergers and acquisitions while flipping the pages of newspapers or browsing the web news. Worldwide, mergers and acquisitions(M&A) are used as instruments in business to gain strength, expand customer base, cut competition or enter into a new market or product segment.
We here will look into what are mergers and acquisitions, the differences between them, and how both affect the stock prices? Read along.
What are Mergers and Acquisitions?
Mergers and acquisitions are often used along interchangeably around but they do hold different meanings if we look at them.
As per the Companies Act,2013, mergers mean the unification of two entities into a single entity. The law also specifies that the desired effect of a merger is to become one business entity and not just the accumulation of assets and liabilities of distinct entities into one.
For say, company ‘X’ and company ‘Y’ merge. After the merger, they become a single entity and continue operating the business operations as planned.
For example,
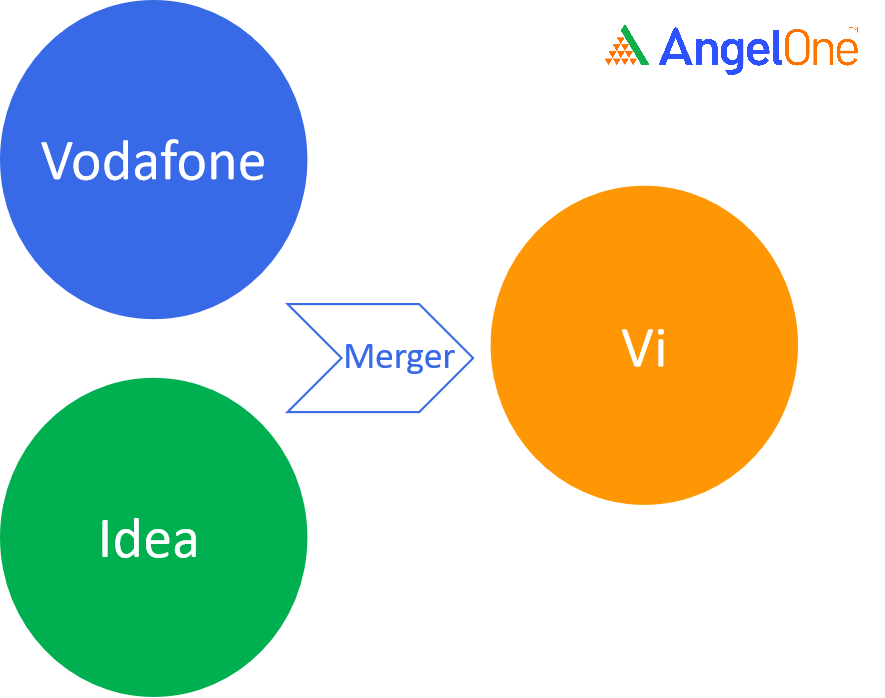
Whereas, acquisitions are situations where one entity buys out the other to combine the bought entity with itself.
If company ‘X’ acquires company ‘Y’, ‘Y’ may cease to exist or continue to become a subsidiary under the parent company ‘X’.
For example,
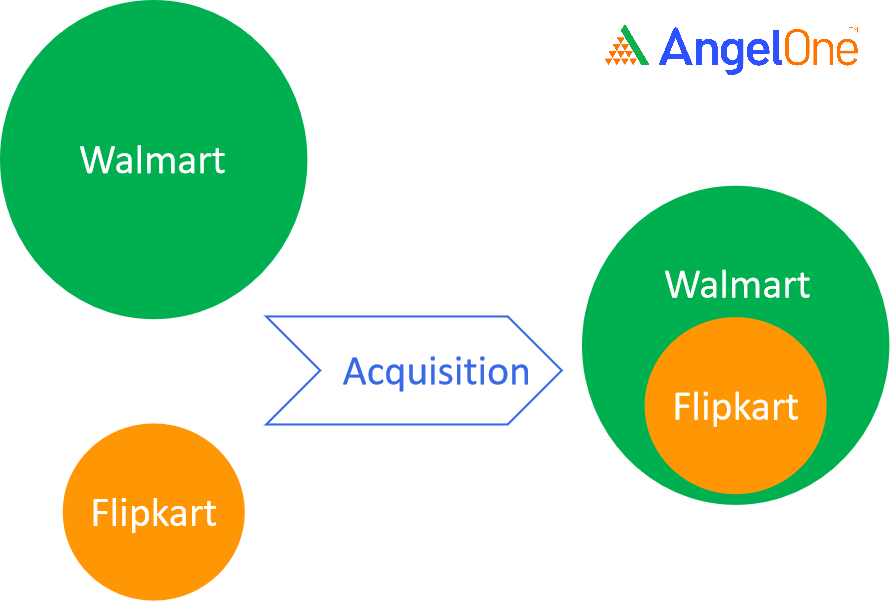
Types of Mergers and Acquisition Companies
Mergers and acquisitions are corporate actions. As investors, it is important to understand mergers vs acquisitions, as both processes alter the corporation’s structure and change the fate of your investment.
Here are the types of mergers that can happen in the corporate world:
Types of Mergers
Vertical: This type of merger happens when two or more companies from different supply chain stages in the same sector combine to form a larger entity. For instance, a manufacturer merging with a distributor or a wholesaler merging with a retailer is an example of a vertical merger.
Horizontal: In horizontal merger action, two or more companies from the same industry and at the same stage of the supply chain or production process combine. If two competing manufacturers collaborate to create a separate entity, it is an example of a horizontal merger.
Conglomerate: A conglomerate merger happens when two companies from unrelated sectors merge to create a larger entity to diversify their business portfolio and increase their market presence.
Congeneric: If two companies operating in related or complementary industries or sectors merge, it forms a congeneric merger. This merger form allows companies to leverage their synergies, expand product and service offerings, and enhance market competitiveness.
Once you have a clear understanding of ‘what is a merger?’, it becomes easier for you to identify each type.
Acquisition Types
Friendly: When the acquirer and the target company mutually agree to the terms and conditions of the acquisition, it results in a friendly acquisition.
Hostile: Sometimes one company bypasses the decisions of the target company’s board and management against acquisition and directly approaches the shareholders or implements aggressive tactics to gain control.
Buyout: In the buyout process, one company may purchase a 51% stake in the target company to gain control over it.
Process
Although there is a difference between merger and acquisition, both processes follow similar steps.
Self-assessment: During the self-assessment phase, the acquiring company reviews the merger needs and examines the consequences. It includes evaluating the strengths, weaknesses, threats, and opportunities before confirming the deal. At this stage, a proper merger strategy is formulated.
Search and screen: At the screening stage, the company may evaluate potential target companies it can acquire at a low price.
Investigate and evaluate: At this stage, the acquiring company conducts detailed analysis, valuation, and due diligence on the target company.
Negotiate and acquire: The representatives of both companies negotiate and finalise the terms of M&A.
Post-merger integration: After the merger, both companies make formal announcements regarding forming a new company. It involves combining and aligning the operations, systems, cultures, and strategies of two companies.
Comparing Merger and Acquisition
Let us take a look into the quick comparison of both:
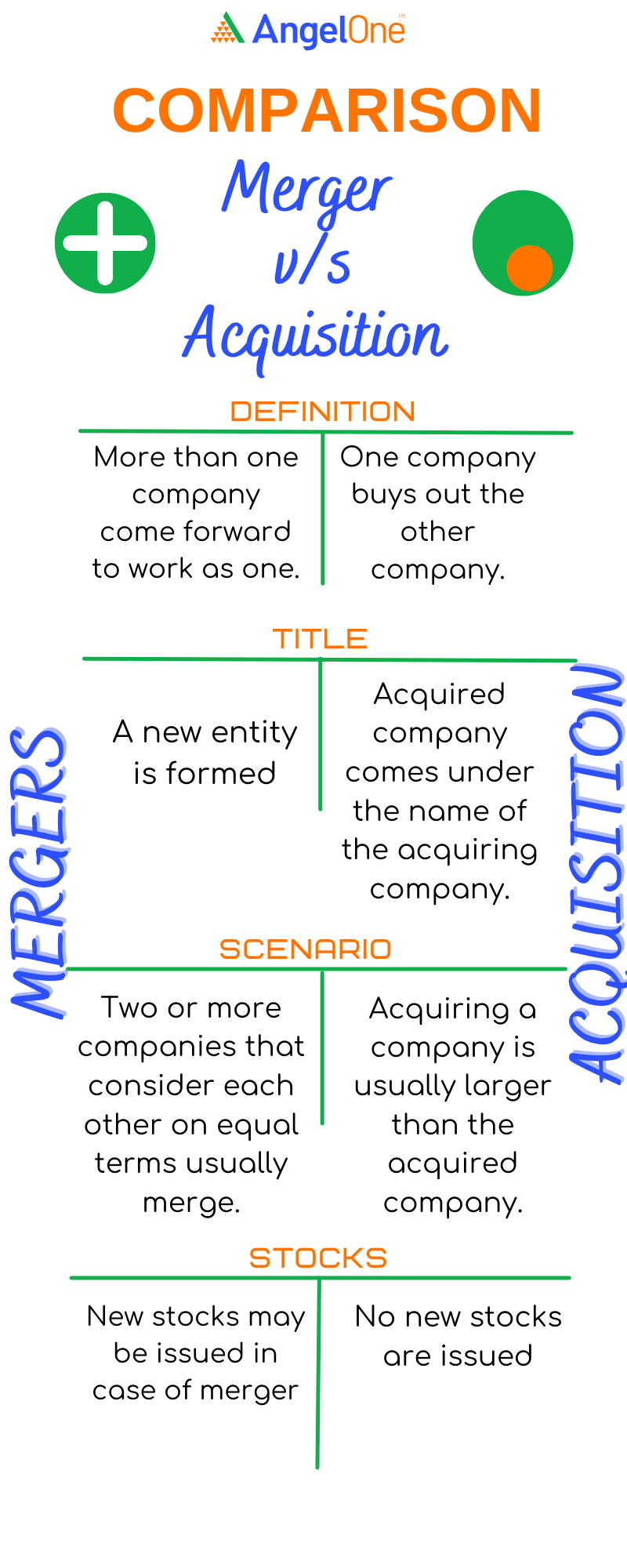
| Basis for comparison | Merger | Acquisition |
| Definition | A process in which more than one companies come forward to work as one. | One company buys out the other company. |
| Title | A new entity is formed. | The acquired company comes under the name of the acquiring company. |
| Scenario | Two or more companies that consider each other on equal terms usually merge. | Acquiring a company is usually larger than the acquired company. |
| Stocks | New stocks may be issued in case of merger | No new stocks are issued |
| Example |
Syndicate Bank merger with Canara Bank. Dena Bank and Vijaya Bank merged with Bank of Baroda
|
|
Why do companies go for Mergers and Acquisitions?
Mergers and Acquisitions may be undertaken for any of the following reasons:
- to enter the new market or product segment
- to access the market through an established brand
- to get a market share
- to eliminate competition
- to reduce tax liabilities
- to acquire competence
- to set off accumulated losses of one entity against the profits of other entity
Mergers and Acquisitions are part of business operations to make their way ahead. Companies either go for mergers or acquisitions considering various factors as seen above. We hope that the article helped you realise how mergers and acquisitions are different from one another.
Merger and acquisition will have quite an impact on stock prices and the stock market. How do mergers and acquisitions affect the stock price of the acquired company and the acquiring company? Will the merger and acquisition announcement lead to volatility of the prices?
Find answers to all your questions on the impact of mergers and acquisitions on stock prices here.
Learn Free Stock Market Course Online at Smart Money with Angel One.
Explore the Share Market Prices Today
| Tata Steel share price | Adani Power share price |
| PNB share price | Zomato share price |
| BEL share price | BHEL share price |
| Infosys share price | ITC share price |
| Jio Finance share price | LIC share price |

