Like every other market, stock market is a place where stocks are traded. For a long time now, stock market has been bringing businesses, investors, traders and other entities together. As an investor, among other things, you should know about the categorization of stocks to determine which stock type suits your investment goals. Here we are to let you know the classification of stocks on different parameters.
We know that stock is a type of security that represents the ownership of a fraction of a company. Stocks are classified into different categories based on the various parameters associated with the company and their performance in the stock market.
Types of stocks
Stocks are classified into different types on various parameters like ownership, market capitalization, risk, sectors, location among others. Below is a representation of types of stocks based on the respective parameters.
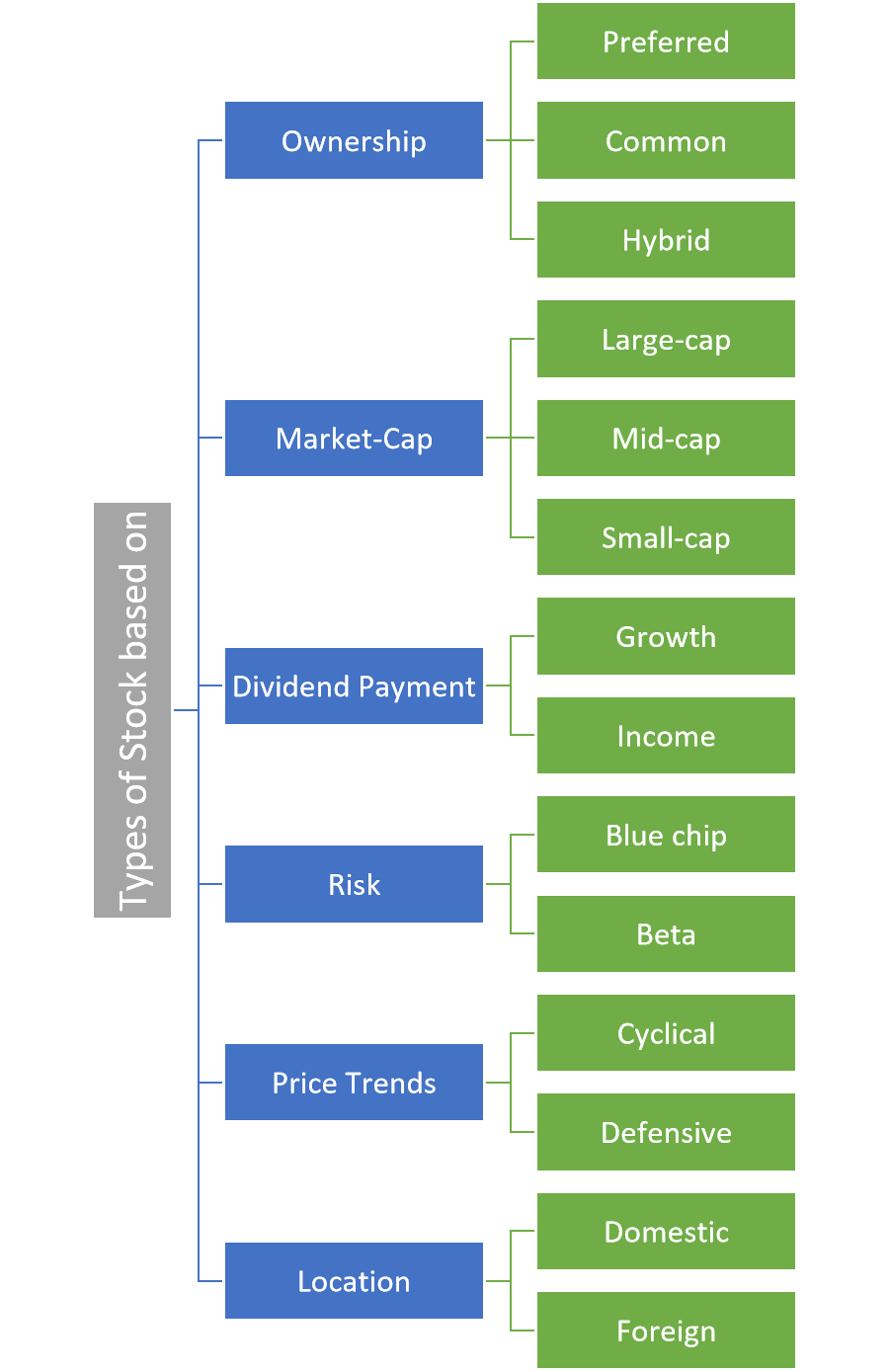
Let us look into each type of stock in detail
1. Types of Stocks Based on Market Capitalisation
Market capitalisation, or "market cap," is a way to classify stocks by the total value of a company's outstanding shares. Here's a clearer look at the different types:
| Large-cap Stocks |
|
| Mid-cap Stocks |
|
| Small-cap Stocks |
|
2. Types of Stocks Based on Ownership
Stocks can be classified based on their rights and privileges, which dictate the level of influence and benefits that shareholders receive. This classification impacts factors such as dividend payments, voting rights, and the priority of claims in case the company faces liquidation.
| Common Stock |
|
| Preferred Stock |
|
| Hybrid Stocks |
|
| Convertible Preference Shares |
|
| Stocks with Embedded Derivative Options |
|
3. Types of Stocks Based on Fundamentals
Investors often evaluate a company's financial health before purchasing its stock, despite the fact that market prices are influenced by supply and demand.
| Overvalued Stocks |
|
| Undervalued Stocks |
|
4. Types of Stocks Based on Price Volatility
Stocks can be classified based on how much their prices fluctuate. Understanding this can help investors choose stocks that match their risk tolerance.
| Beta Stocks |
|
| Blue-chip Stocks |
|
5. Types of Stocks Based on Economic Trends
Stocks respond differently to changes in the economy. They can be categorised based on their reaction to economic trends.
| Cyclical Stocks |
|
| Defensive Stocks |
|
There are various other parameters like sectors, fundamentals, etc. based on which the stocks are classified. Classification of stocks on different parameters helps you determine the nature of stocks which in turn helps make a better decision. Now that you know the classification of stocks, you can choose the stocks that suit your investment needs. Also, you can refer to types of orders to know the various orders you can place to buy/sell stocks of your choice.
How to Buy Stocks?
Various criteria, such as company size, dividend payment, industry, risk, volatility, and fundamentals, can be used to categorise stocks. The following details the methods for buying equities based on these classifications:
- Create the necessary accounts: Before you begin stock trading, you must first create a demat and trading account. Without these accounts, participation in stock markets is not possible.
- Conduct Stock Analysis: Analyse stocks based on various parameters such as company size, dividend payments, industry, risk, volatility, and fundamentals. Tailor your choices to fit your investment profile.
- Monitor Selected Stocks: After selecting potential stocks, monitor them for a period to ensure informed buying decisions. Understanding stock price movements is crucial during this phase.
- Determine Order Placement Timing: Choose whether to place your order during market hours or after markets close. Consider the target share price and preferred buying conditions.
- Choose Order Type: Order options encompass limit orders, market orders, and stop-loss orders. Each order type serves a specific purpose, providing flexibility in executing transactions.
- Execute Order through Trading Account: Once order specifics are determined, execute the trade through your online trading account or by contacting your broker. Provide necessary bank account details for the seamless processing of purchase funds.
- Verify order Execution: Confirm that your order was properly performed and that the purchase amounts were deducted from your bank account. This completes the process of purchasing stocks and creates your ownership of the chosen assets.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of stocks in India, including large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap, common, preferred, income, and growth stocks, is crucial for making informed investment decisions. Whether you seek stability with blue-chip stocks, higher returns with growth stocks, or steady income with dividend-paying stocks, knowing these categories will enhance your investment strategy and help you navigate the stock market more effectively. Happy investing!
Explore the Share Market Prices Today
| IRFC share price | Suzlon share price |
| IREDA share price | Tata Motors share price |
| Yes Bank share price | HDFC Bank share price |
| NHPC share price | RVNL share price |
| SBI share price | Tata Power share price |

