When a company invests in another company in a foreign land, the investment is said to be a foreign direct investment (FDI). The FDIs are further categorised into four types. Read on to find out what they are.
The investment market is an enormous space. Individual investors and large companies can invest in companies within their countries as well as overseas. When one company invests in a business in another company in a foreign land, the investment is deemed as foreign direct investment or FDI.
How Does FDI Work?
- Investment Types: Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) can involve either organic investments, where a foreign company expands its existing business in a new country, or inorganic investments, where a foreign company acquires a local business. This allows them to establish a physical presence, unlike portfolio investments which involve buying stocks or bonds without directly controlling the company.
- Economic Impact: FDI is particularly beneficial for developing economies. It injects much-needed capital into businesses, potentially reviving struggling companies and creating new jobs. This can lead to increased productivity, technological advancements, and overall economic growth.
- Government Incentives: Many governments, like India, actively attract FDI by offering incentives in specific sectors like defense, telecommunication, and IT. These incentives can include tax breaks, relaxed regulations, and infrastructure development support.
- Benefits Beyond Debt: Unlike loans, FDI doesn't burden the recipient country with debt. This non-debt financial resource can significantly boost economic growth.
- Global Drivers: Globalisation and internationalisation paved the way for FDI. Additionally, foreign companies may invest to:
- Gain control over foreign operations and establish a brand presence in new markets.
- Foster competition and break up monopolies, benefiting local consumers with wider choices and potentially lower prices.
- Mitigate risks associated with economic downturns in their home countries by diversifying their operations and income streams.
Types of Foreign Direct Investments
1. Horizontal FDI
The most common type of FDI is Horizontal FDI, which primarily revolves around investing funds in a foreign company belonging to the same industry as that owned or operated by the FDI investor. Here, a company invests in another company located in a different country, wherein both the companies are producing similar goods. For example, the Spain-based company Zara may invest in or purchase the Indian company Fab India, which also produces similar products as Zara does. Since both the companies belong to the same industry of merchandise and apparel, the FDI is classified as horizontal FDI.
2. Vertical FDI
Vertical FDI is another type of foreign investment. A vertical FDI occurs when an investment is made within a typical supply chain in a company, which may or may not necessarily belong to the same industry. As such, when vertical FDI happens, a business invests in an overseas firm which may supply or sell products. Vertical FDIs are further categorised as backward vertical integrations and forward vertical integrations. For instance, the Swiss Coffee producer Nescafe may invest in coffee plantations in countries such as Brazil, Columbia, Vietnam, etc. Since the investing firm purchases, a supplier in the supply chain, this type of FDI is known as backward vertical integration. Conversely, forward vertical integration is said to occur when a company invests in another foreign company which is ranked higher in the supply chain, for instance, a coffee company in India may wish to invest in a French grocery brand.
3. Conglomerate FDI
When investments are made in two completely different companies of entirely different industries, the transaction is known as conglomerate FDI. As such, the FDI is not linked directly to the investors business. For instance, the US retailer Walmart may invest in TATA Motors, the Indian automobile manufacturer.
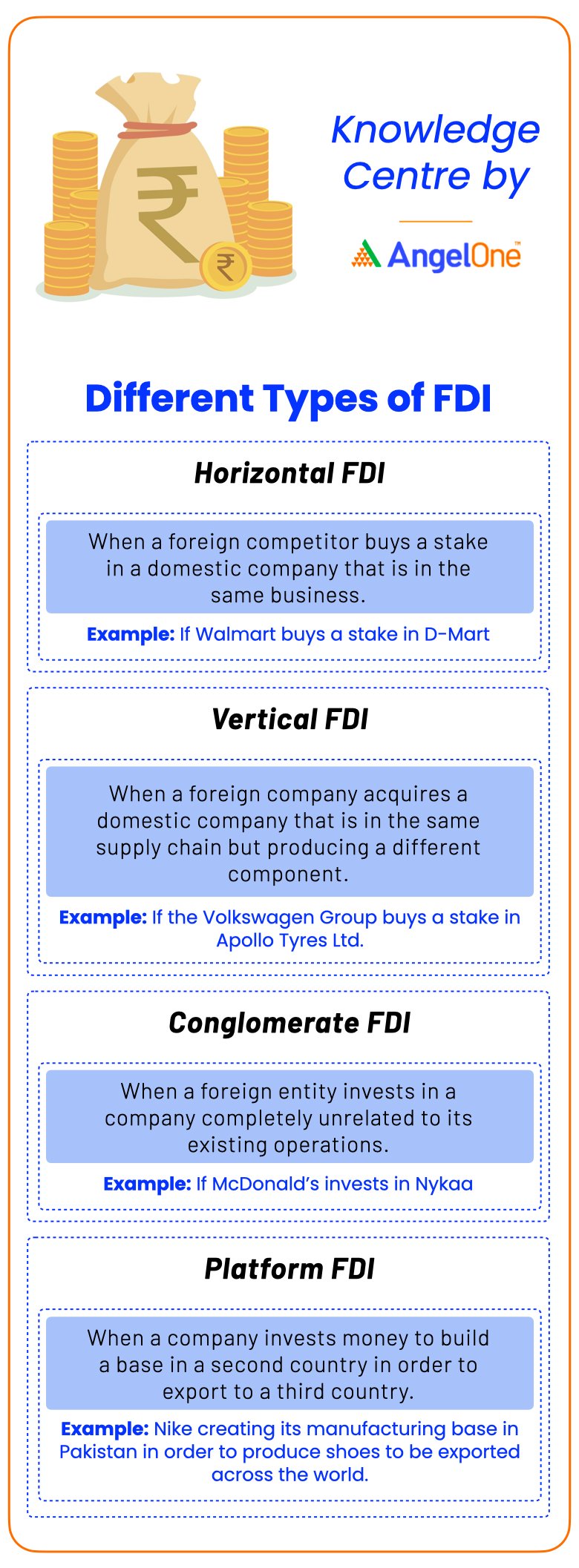
4. Platform FDI
The last types of foreign direct investment is platform FDI. In the case of platform FDI, a business expands into a foreign country, but the products manufactured are exported to another, third country. For instance, the French perfume brand Chanel set up a manufacturing plant in the USA and export products to other countries in America, Asia, and other parts of Europe.
If you intend to invest via FDI, you must know about the different types of FDI with examples. With FDI, the money invested can be used to start a new business in a foreign country or to invest in an already existing business in a foreign country. For more information on FDIs, consult Angel One advisors.
Conclusion
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) presents a compelling opportunity for investors seeking to expand their reach beyond domestic markets. By understanding the four main FDI types - horizontal, vertical, conglomerate, and platform - you can tailor your investment strategy to specific goals. FDI offers a versatile tool for achieving your investment objectives. Conduct thorough research and consult with financial advisors to navigate the intricacies of FDI and unlock its full potential for growth.

