When it comes to economic growth, capital is a vital ingredient. As most nations cannot meet their total capital requirements through their internal resources only, they turn towards foreign investors. These investors use two means to invest in the overseas economy: foreign direct investment (FDI) and foreign portfolio investments (FPI). These are the two most common ways for investors to put their money into international portfolios. But what is the difference between FDI vs FPI? When it comes to what is implied by FDI vs portfolio investments in foreign assets, there are many differences. Let's clarify these differences by defining FDI vs FPI.
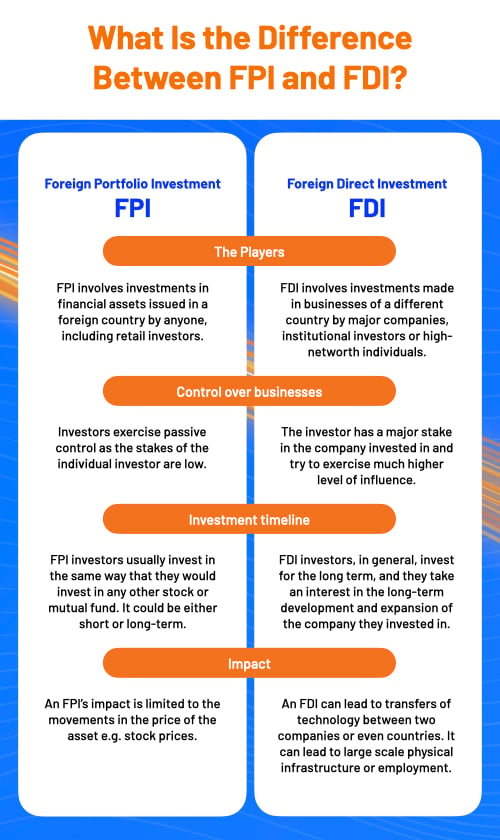
FDI implies that foreign investors are directly investing in the productive assets of another nation. On the other hand, FPI implies investing in financial assets like the bonds and stocks of another country. While there are commonalities between FDI vs portfolio investments, they are also different in many ways. Since retail investors have started investing in both these types of foreign investments, they should be clearly aware of the difference between FDI vs FPI. Nations with a higher level of FPI can easily encounter are higher market volatility and turmoil with respect to currency during uncertain times.
Difference between FDI vs FPI
Although both FPI and FDI are foreign investments at their heart, there are fundamental differences between the two that should be taken into account before investing.
1. Degree of Control for FDI vs FPI
The primary difference is the degree of control the foreign investor can exercise. Investors who look into FDI can usually exercise a higher degree of control than those who invest in FPI. FDI investors take controlling positions in two ways: either through joint ventures or in domestic firms. In general, FDI investors are actively involved in the management of their investments.
On the other hand, FPI investors are not as involved. They tend to take on more passive positions in their investments. They are considered passive investors as they are not involved in the day-to-day functioning and operation as well as strategic planning required by any domestic companies. Even if the investor has a controlling interest in the company, a foreign portfolio investment will lend them passive shares. Hence, the degree of control is an important difference between FDI vs portfolio investments.
2. Investment Horizon of FDI vs FPI
Another key difference to point out is that foreign direct investors tend to take a longer-term approach to their FDI investments. It can take anywhere between 6 months to a couple of years to advance from the planning stage to the project implementation stage. The difference with respect to foreign portfolio investments is that the investors for these types of foreign investments have a much shorter investment horizon to worry about. They may be invested for the long haul however, the investment horizon continues to remain small, especially when one’s local economy is turbulent. The second point of difference between FDI vs FPI is closely tied to the third difference.
3. Liquidity of FDI vs FPI investments
FDI investments are carried out with a longer horizon in mind as investors usually do not liquidate their assets and depart from the nation. FDI assets can even be considered larger and definitely less liquid than FPI assets. Lack of liquidity reduces the buying power of an investor and increases the risk somewhat. This is why investors plan so much before investing in these types of illiquid assets. FPI assets are both widely traded and highly liquid. An FPI investor has the luxury of exiting their investment with a few clicks of their mouse. Hence, these types of investments do not require as much planning and may also be considered more volatile due to being highly liquid.
4. Volatility of FDI vs FPI investments
The liquidity of an asset is a factor of how widely traded it is and also how volatile it is. FDI can prove to be a more stable investment than FPI, especially for a nation to attract foreign investment. This is because foreign direct investments require a longer investment horizon. An investor is somewhat locked into their investment for the long haul due to the lack of liquidity. FPI can be traded away in a day’s time and so can prove to be more volatile due to traders constantly entering and leaving their positions with the option of liquidity available to them.
5. Nature of investment
Usually, an FDI is a long-term investment in another country. It typically includes direct ownership of infrastructure, factories, and subsidiaries. Conversely, FPI involves investing in financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, commodities, ETFs, etc. FPI doesn't offer direct ownership or control over the underlying asset.
6. Objective
FDI and FPI serve different purposes for the investing party. FDI allows investors to have a lasting impact and gain strategic advantages in the host country. Companies engage in FDI to gain benefits like market expansion, economies of scale, and favourable business conditions. FPI investors focus more on receiving profits from their investments and capitalising on short-term market opportunities.
7. Risks and returns
Foreign direct investment involves higher risk due to its long-term nature and direct involvement in resource development. However, FDI also has the potential to generate higher returns over the long run. Compared to that, FPIs are short investments with higher liquidity. But returns on FPI are exposed to market volatility.
8. Impact on the economy
FDI investments have a higher degree of influence on the growth and development of the host country. It brings in capital, creates employment, facilitates technology transfer, and promotes infrastructure development.
Conversely, foreign portfolio investment focuses on capitalising on the host country’s financial market opportunities. It contributes to market efficiency, increases liquidity, and provides capital for companies. But it may have a limited impact on the broader economy.
FDI vs FPI
Here is a table to help you understand the differences between FDI and FPI.
| Parameters | FDI | FPI |
| Definition | FDI refers to direct investment made by foreign investors in obtaining infrastructure, factories, subsidiaries, etc. in the host country. | Foreign Portfolio Investments (FPI) involves investing in financial securities, such as stocks, bonds, etc. in a foreign country. |
| Role of investors | Active investor | Passive investor |
| Type of investment | Direct investment | Indirect investment |
| Degree of control | More control over investment | Very little control |
| Term | Long-term investment | Short-term investment to capitalise on market movements |
| Risk | Stable risk | Highly volatile due to market fluctuations |
| Impact | Have a direct impact on the host country’s growth and development. | Contributes to market efficiency, improves liquidity etc. |
Learn Free Stock Market Course Online at Smart Money with Angel One.
Explore the Share Market Prices Today
| Tata Steel share price | Adani Power share price |
| PNB share price | Zomato share price |
| BEL share price | BHEL share price |
| Infosys share price | ITC share price |
| Jio Finance share price | LIC share price |