Among the known corporate actions, Bonus issues and Stock Split are two measures undertaken by companies to boost the number of shares. In both cases, the number of shares with the shareholders will be enhanced without paying any extra amount. However, the objectives of both the concepts are different and here we are to let you know the difference.
What is a Bonus Issue?
Bonus Issue also known as Capitalization Issue, offers additional shares to the existing shareholders without any cost. Companies when they have a profitable turnover, use this method to reward their shareholders. They are issued out of the reserves of the company.
Bonus shares are distributed in proportion to an investor’s shareholdings. For instance, when a firm offers 5:1 bonus shares, it means that for every 5 shares held in your Demat account ( as on the record date), the shareholder will receive 1 bonus share. So, if you hold 100 shares of that firm, you will receive 20 bonus shares.
To illustrate the effect on the shares of an existing shareholder of a company, let us assume a bonus issue of different ratios – 1:5, 1:1 and 5:1
|
Before Bonus Issue |
After Bonus Issue |
|||||||
|
Bonus Issue |
No. of shares held |
Share Price |
Face Value |
Value of Investment |
No. of shares held |
Share Price |
Face Value |
Value of Investment |
|
5:1 |
100 |
10 |
10 |
1000 |
120 |
8.333 |
10 |
1000 |
|
1:1 |
100 |
100 |
10 |
10000 |
200 |
50 |
10 |
10000 |
|
1:5 |
2000 |
20 |
10 |
40000 |
12000 |
3.33 |
10 |
40000 |
By issuing bonus shares, the number of outstanding shares increases with a proportional decrease in the value of each share ensuring no change in the market capitalization as shown in the table above. However, the face value of the shares remains unchanged.
Many companies see bonus issues as a viable alternative to dividends. Bonus issues are payments made to shareholders from a company’s net reserves while dividends are paid out from net profits. Dividends are paid to shareholders in the form of cash which gets credited to your registered bank account (linked to Demat account), while bonus issues are paid in additional shares. As a result, it increases the value of its stock, making it more enticing to investors.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bonus Shares
Advantages of Bonus Shares:
Tax Benefits: Investors benefit from bonus shares as they are exempt from paying taxes on these shares upon receipt. This can be particularly appealing for long-term shareholders aiming to amplify their investments without incurring immediate tax liabilities.
Investment Growth: For long-term investors, bonus shares provide an effective way to increase their holdings in a company. This can be especially beneficial for those looking to grow their investment over time.
Boosts Investor Confidence: The issuance of bonus shares can enhance investor confidence in the company's operations and prospects. It demonstrates that the company is reinvesting its cash reserves into business expansion, signaling a positive outlook.
Higher Future Dividends: Holding a larger number of shares through bonus issues means that investors could receive higher dividends in the future, provided the company declares dividends.
Positive Market Signals: Issuing bonus shares often sends a positive message to the market, reflecting the company's commitment to long-term growth and stability. This can improve the company’s reputation and attract more investors.
Disadvantages of Bonus Shares:
Increased Volatility: The announcement and issuance of bonus shares can lead to increased market speculation and sentiment changes, contributing to greater stock price volatility.
Capital Allocation: Allocating additional shares requires the company to use more of its cash reserves. This capital allocation might have otherwise been distributed as dividends to shareholders.
Unchanged Profits: Despite the increase in the number of shares, the company's overall profit remains unchanged. This results in a proportional decrease in earnings per share (EPS), which might not be favourable for all investors.
What is a Stock Split?
A stock split is an action taken in which a company divides its existing shares into multiple shares to boost the liquidity of shares. Split is usually undertaken when the stock price is high, making it pricey for investors to acquire. It brings down the share price as the number of shares increases. The market cap of the firm and the value of each shareholder’s investment stay unchanged after a stock split.
Like Bonus Issues, the price gets decreased by the ratio. To illustrate,
|
Before Split |
After Split |
|||||||
|
Stock split |
No. of shares held |
Share Price |
Face Value |
Value of Investment |
No. of shares held |
Share Price |
Face Value |
Value of Investment |
|
1:2 |
10 |
900 |
10 |
9000 |
20 |
450 |
5 |
9000 |
|
1:5 |
10 |
900 |
10 |
9000 |
50 |
180 |
2 |
9000 |
However, the face value of the share changes with the stock split. If the face value of a stock is Rs 10, and the stock is split in the ratio 1:2, the face value of the stock after the stock split becomes Rs 5.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Stock Split
Advantages of Stock Split:
Increase in Outstanding Shares: A stock split significantly increases the total number of outstanding shares, though the company's market capitalisation remains the same. This does not change the company's overall value but makes the stock more accessible.
Reduced Share Price: A stock split makes the stock more affordable for individual investors by proportionally reducing the share price. This can attract a broader range of investors who might have been previously priced out.
Enhanced Accessibility: With more shares available at a lower price, acquiring and selling shares is easier. This increased liquidity can make the stock more attractive to retail and institutional investors.
Simplified Portfolio Management: The lower share price and higher share volume make it easier for investors to diversify and rebalance their portfolios. More shares at a lower price provide flexibility in managing investments.
Avoiding Dilution: Instead of issuing new shares, companies can increase the number of shares through a stock split. This strategy helps prevent stock dilution and maintain the ownership percentage of existing shareholders.
Disadvantages of Stock Split:
Cost and Regulatory Compliance: Conducting a stock split involves significant costs and must adhere to legal and regulatory requirements. This can be a resource-intensive process for the company.
No Impact on Company Value: A stock split does not affect the company’s fundamental position. It does not add any intrinsic value and is merely an accounting adjustment to the number of shares and their price.
Potential for Increased Volatility: The new, lower share price post-split may attract more investors, increasing the stock’s accessibility. This influx can lead to higher volatility as more investors buy and sell the stock.
Differences between Bonus Issue and Stock Split
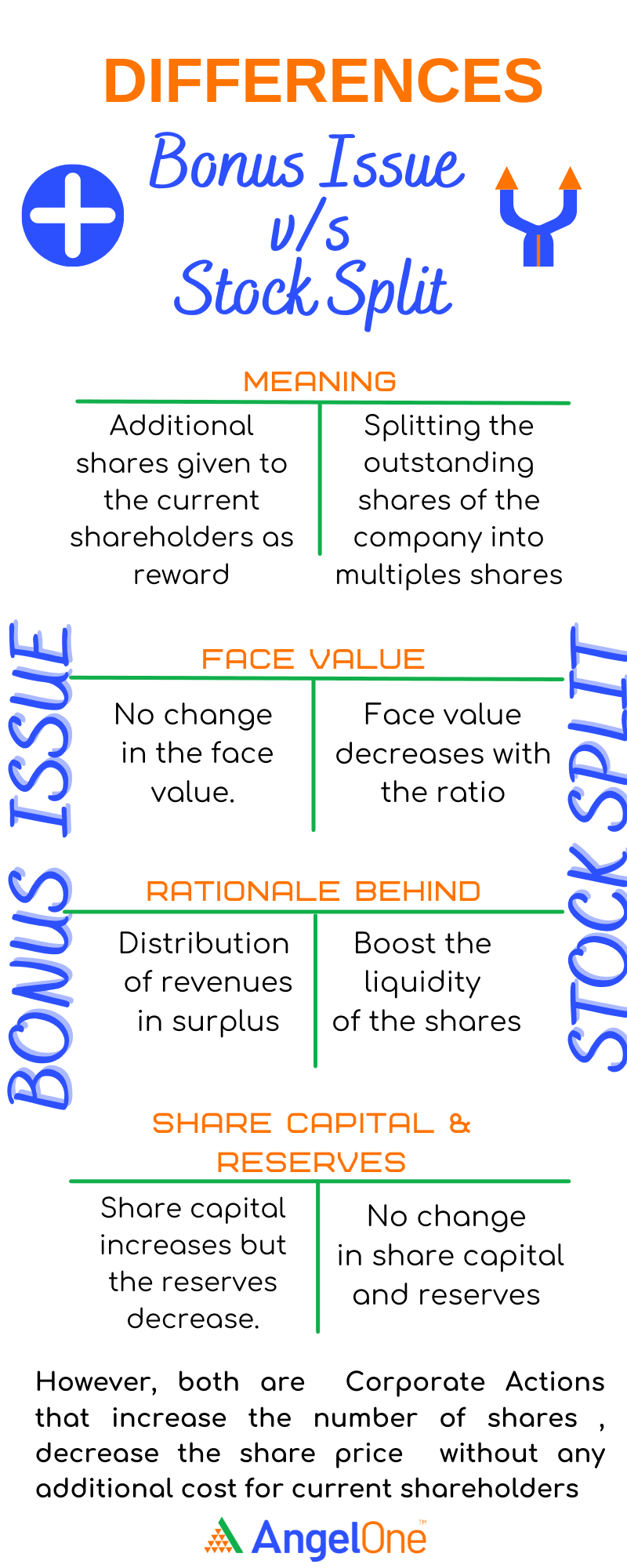
| Basis | Bonus Issue | Stock Split |
| Meaning | Additional shares given to the current shareholders | Splitting the outstanding shares of the company into multiple shares |
| Face Value | No change | Decreases as per the ratio |
| Rationale | Distribution of reserves and surplus | Boost the liquidity of the shares |
| Share Capital and Reserves | Share capital increases but Reserves decrease | No change |
Both Bonus Issue and Stock Split are effective ways to attract retail participation by increasing the number of shares and reducing the share prices. The existing shareholders in both cases will get to increase their number of shares without paying any extra amount. However, they differ in their rationale, affecting the face value, and reserves and surplus of the company as seen above. Either a Bonus Issue or Stock Split, the number of shares increases, the share price decreases without change in the value of investment of existing shareholders and market capitalisation of the company.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between Bonus Issues and Stock Splits helps investors make informed decisions. Both methods increase the number of shares and reduce share prices, making them more accessible to investors. However, they differ in their impact on face value and company reserves. Take advantage of these opportunities by starting your investment journey today. Open a Demat account with Angel One and gain access to a wealth of resources and tools to grow your portfolio. Sign up now!

